Lower back when bending over is a typical problem that influences a sizeable portion of the population sooner or later in their lives. This pain can range from a slight nuisance to a debilitating condition that hinders daily sports activities. Understanding the underlying motives, recognizing the signs and symptoms and signs and symptoms, and exploring treatment options are critical for managing and stopping decreased all-over again pain.
Understanding Lower Back Pain When Bending Over
Lower again ache is soreness located within the lumbar location of the backbone. It can be categorized into the most essential types:
- Acute Lower Back Pain: This type lasts for some days to weeks and is often related to a particular incident or damage.
- Chronic Lower Back Pain: This kind persists for over three months and may stem from ongoing problems, such as degenerative illnesses or chronic conditions.
Prevalence
Lower aches are one of the fundamental reasons for incapacity worldwide, affecting people of each age. It can considerably impact your extraordinary life, leading to unnoticed workdays and reduced productivity.
Bases for Lower Back Pain When Bending Over
Several elements can contribute to decreasing back pain while bending over. Identifying those causes is critical for effective remedy and prevention.
1. Muscle Strain
Muscle strain happens when the muscle mass inside the decrease again is overstretched or torn. This can result from lifting heavy items improperly or sudden moves. Muscle pressure is a common motive of lower back pain when bending over and usually heals with relaxation and conservative treatments.
2. Ligament Sprain
Ligaments are brutal bands of tissue that are part of bones. A sprain occurs when those ligaments are stretched or torn, frequently because of excessive stress or sudden movements. Ligament sprains can cause massive aches and instability in the Lower back pain when bending over.
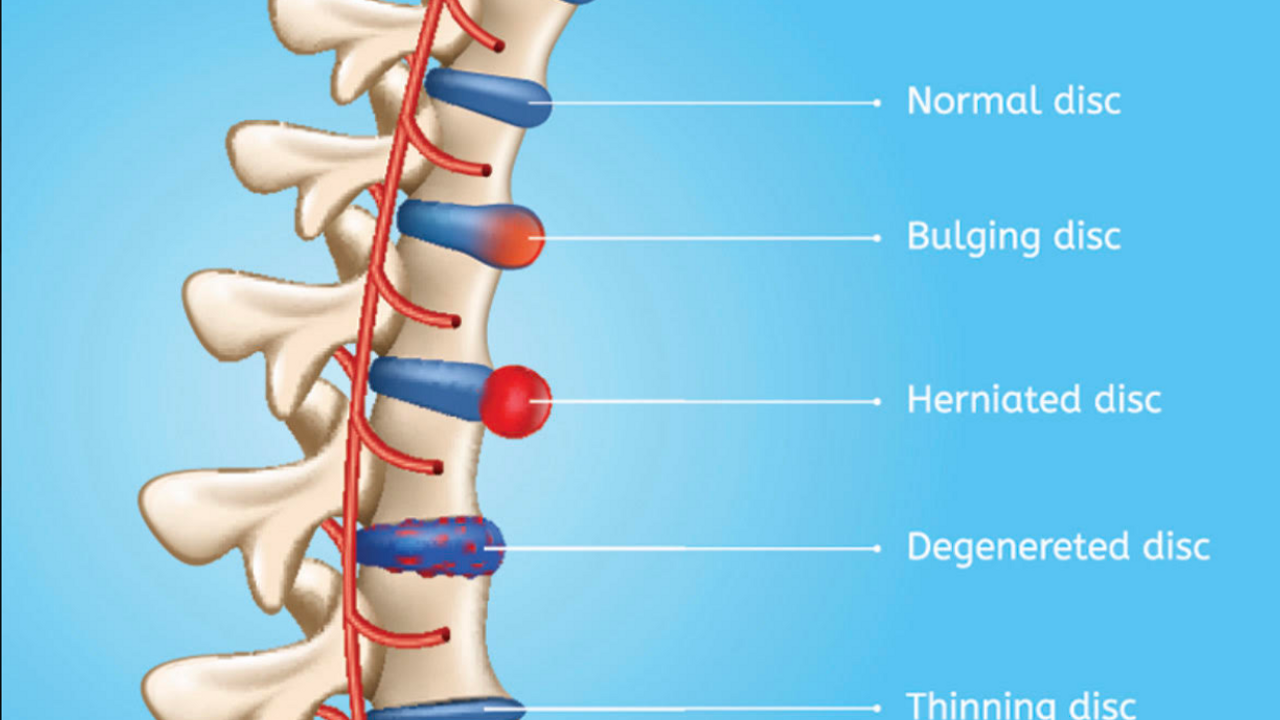
3. Herniated Disc
A herniated disc occurs at an equal time as the soft, gel-like middle of a spinal disc pushes through a tear inside the outer layer. This can press on nearby nerves, inflicting pain, numbness, and inclined points in the lower back and legs. Herniated discs continually have the effect of wear and tear and tear and tear or surprising damage.
4. Sciatica
Sciatica is characterized by the beneficial resource of pain released alongside the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the decreased lower back through the hips and down every leg. Bending over can exacerbate sciatica signs, foremost to sharp, capturing pain.
5. Poor Posture
Maintaining horrific posture over the years can strain the muscle agencies, and ligaments within the decrease returned. Bending over in the wrong shape can exacerbate this pressure, primarily causing pain.

6. Degenerative Disc Disease
As people age, the spinal discs can lose hydration and elasticity, critical to degenerative disc illness. This can cause persistent Lower back pain when bending over, particularly when bending over.
Risk Factors
Several risk elements can boost the probability of a growing decrease in returned aches:
- Age: The risk of lower back pain when bending over will increase because of degenerative modifications inside the backbone.
- Physical Activity: A lifestyle and excessive bodily pastime can contribute to back pain.
- Occupational Hazards: Jobs containing heavy lifting, extended sitting, or repetitive actions can increase the risk of lower back pain when bending over.
- Obesity: Excess frame weight can place more significant strain on the decreased lower back, leading to aches and pain.
Symptoms Associated with Lower Back Pain When Bending Over
A lower decrease in pain can observed in several tactics, depending on the underlying motive. Common symptoms and signs and symptoms consist of:
- Pain Characteristics: The pain may be stupid, aching, sharp, or stabbing.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that releases down the portions also suggests nerve involvement at the side of sciatica.
- Numbness and Tingling: These symptoms can arise if a nerve is compressed or angry.
- Weakness: Weakness in the legs or decreased return can result from nerve harm or muscle pressure.
Diagnosis
Accurate analysis is essential for effective treatment. The diagnostic way might also embody the following:
- Medical History: A unique fact permits findinging capacity causes and contributing elements.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination assesses motion, posture, and reflexes to pinpoint the ache supply.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans provide specific photographs of the spine to perceive structural troubles.
Treatment Options
Conservative Treatments
- Rest and Activity Modification: Short intervals of rest, determined through a sluggish go lower back to sports activities, can assist in alleviating aches.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored physical activities and stretches strengthen the returned and beautify flexibility.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory capsules, and muscle relaxants can offer quick treatments.
Interventional Treatments
- Injections: Steroid injections can lessen inflammation and aches.
- Surgery: In severe instances, surgical interventions can be critical to address structural troubles accurately.
Home Remedies and Self-care
1. Ice and Heat Therapy
Alternating between ice packs and warm pads can lessen inflammation and relax muscle tissues. Ice is generally used in the preliminary stages of injury to reduce swelling, while heat can help soothe and loosen tight muscle mass.
2. Gentle Stretching Exercises
Stretching sports can alleviate muscle tension and decorate flexibility. Simple stretches, including knee-to-chest and hamstring, can help relieve decreased Lower back pain when bending over.
3. Proper Ergonomics and Posture
Maintaining desirable posture and ensuring ergonomic workspaces can prevent stress at the lower back. This includes using chairs that guide the herbal curve of the backbone and positioning laptop screens at eye level.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing decreased returned pain includes incorporating healthy habits into day-by-day life:
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening core muscle groups supports the backbone and reduces the threat of harm.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess weight minimizes strain on the decreased back.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Using the legs to raise in place of the again prevents accidents.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Adjusting workspaces to sell appropriate posture reduces the danger of decreased back pain.
When to See a Doctor
It’s essential to seek scientific attention if:
- Pain persists for several weeks.
- There is a severe ache that doesn’t enhance with relaxation.
- Pain radiates down the legs or causes a weak point.
- Control over one’s bowels or bladder is lost.
Coping with Chronic Lower Back Pain When Bending Over
Managing persistent aches includes a combination of clinical lifestyle changes:
- Pain Management Techniques: Remedy, physical therapy, and opportunity cures like acupuncture.
- Mental Health Considerations: Chronic pain ought to affect intellectual well-being. Techniques such as mindfulness, reflection, and counseling can support managing the emotional impact of continual aches.
Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths about decreased back ache:
- Myth: Rest is an excellent treatment for back aches.
- Fact: While rest can assist to start with, extended inaction can worsen the situation.
- Myth: Only older people get more pain.
- Fact: Lower back pain when bending over aches can affect people of every age.
Conclusion
Lower back pain when bending over aches while bending over can appreciably affect lifestyles; however, they could be managed effectively with the proper method. Understanding the reasons, threat elements, and treatment alternatives is essential for locating comfort and stopping destiny episodes. By incorporating preventive measures and searching for appropriate hospital therapy, you could maintain a healthful and ache-unfastened again.

