The Best 1 Deadlift Variations to Must Try
Deadlifting is a staple workout in electricity education, recognized for its capability to construct electricity, decorate muscle groups, and enhance typical health. While the traditional deadlift is the most well-known, numerous variations of a kind muscle businesses cater to unique education dreams. This comprehensive manual explores various deadlift variations, their advantages, and how to perform every one efficiently.
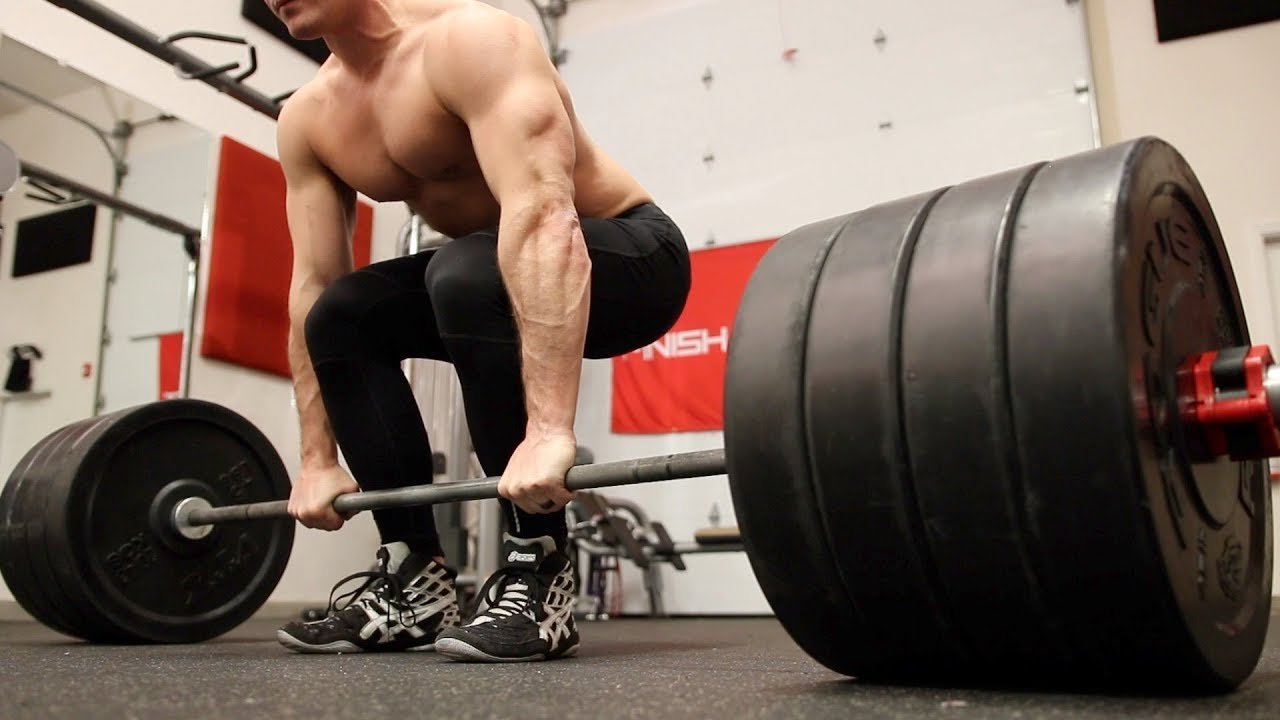

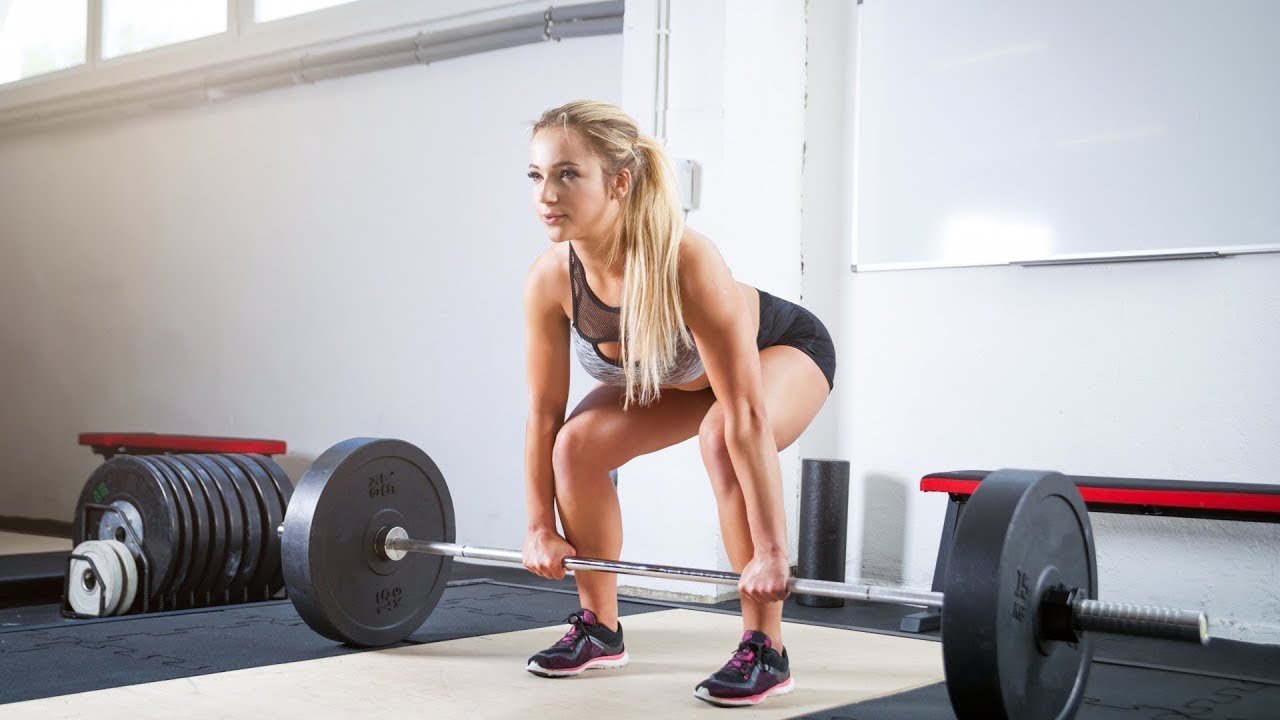
Traditional Deadlift
What is the Traditional Deadlift Variations?
The deadlift variations involves raising a packed barbell from the ground to standing, emphasizing the posterior chain muscular tissues, including the hamstrings, glutes, and lower back.
Benefits of Traditional Deadlift Variations
- Strengthens the Posterior Chain: This exercise targets critical muscle tissue in the lower back of the frame, which is vital for average electricity and balance.
- Improves Grip Strength: Holding heavy weights complements grip patience.
- Enhances Core Stability: Requires sturdy centre engagement to maintain the right shape.
How to Perform a Traditional Deadlift
- Setup: Stand with ft hip-width aside, feet pointing ahead. The barbell ought to be over your mid-foot.
- Grip the Bar: Bend on the hips and knees, and grip the bar just out of the doors on your knees.
- Lift: Engage your middle, straighten your lower back, and raise the bar by extending your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the movement to lower the bar and return to the floor, retaining management.
Sumo Deadlift Variations
What is the Sumo Deadlift?
The sumo deadlift has a much broader view, with toes pointing outwards and fingers placed within the knees. This version reduces the range of motion and emphasizes the quads and hips.

Benefits of Sumo Deadlifts
- Reduces Stress on Lower Back: The wider stance and upright torso position can alleviate lower back pressure.
- Targets Inner Thighs: Greater activation of the adductors and internal thigh muscle tissue.
- Enhances Hip Mobility: Promotes flexibility and power within the hips.
How to Perform a Sumo Deadlift
- Setup: Stand with a considerable stance, toes pointed outwards. The barbell should be over your mid-foot.
- Grip the Bar: Bend your knees at the hips and knees and grip the bar interior.
- Lift: Engage your centre, straighten your back, and lift the bar by expanding your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the movement to lower the bar again to the ground with control.
Romanian Deadlift (RDL)
What is the Romanian Deadlift Variations?
The Romanian deadlift focuses more on the eccentric (reducing) phase and emphasizes the hamstrings and glutes. Unlike the traditional deadlift, the RDL begins offevolved from a standing feature and includes a slight bend inside the knees.
Benefits of Romanian Deadlifts
- Hamstring Emphasis: Increased activation of the hamstrings in the evaluation of conventional deadlifts.
- Improves Hip Hinge Mechanics: Excellent for studying the hip hinge motion.
- Enhances Flexibility: Promotes flexibility in the hamstrings and lower returned.
How to Perform a Romanian Deadlift
- Setup: Stand with feet hip-width apart, maintaining the barbell with an overhand grip.
- Lower the Bar: With a moderate knee bend, hinge at the hips and decrease the bar down the front of your legs.
- Lift: Engage your hamstrings and glutes to raise the bar and return to the starting role.
Stiff-Legged Deadlift Variations
What is the Stiff-Legged Deadlift?
The stiff-legged deadlift is like the RDL; however, it entails keeping the legs nearly instantly. This version similarly isolates the hamstrings and decreases returned.
Benefits of Stiff-Legged Deadlifts
- Isolates Hamstrings: Provides a deep stretch and more muscular contraction within the hamstrings.
- Strengthens Lower Back: Greater emphasis on lower back muscle groups.
- Increases Flexibility: Encourages the posterior chain to be more bendy.
How to Perform a Stiff-Legged Deadlift
- Setup: Stand with ft hip-width aside, shielding the barbell with an overhand grip.
- Lower the Bar: Keep your legs directly, hinge at the hips and lower the line down the front of your legs.
- Lift: Engage your hamstrings and lower lower back to boost the bar again to the starting position.
Trap Bar Deadlift Variations
What is the Trap Bar Deadlift?
The trap bar deadlift uses a hexagonal bar that allows you to step indoors. This variant modifies the mechanics of the raise, decreasing pressure at the lower back and emphasizing the quads.
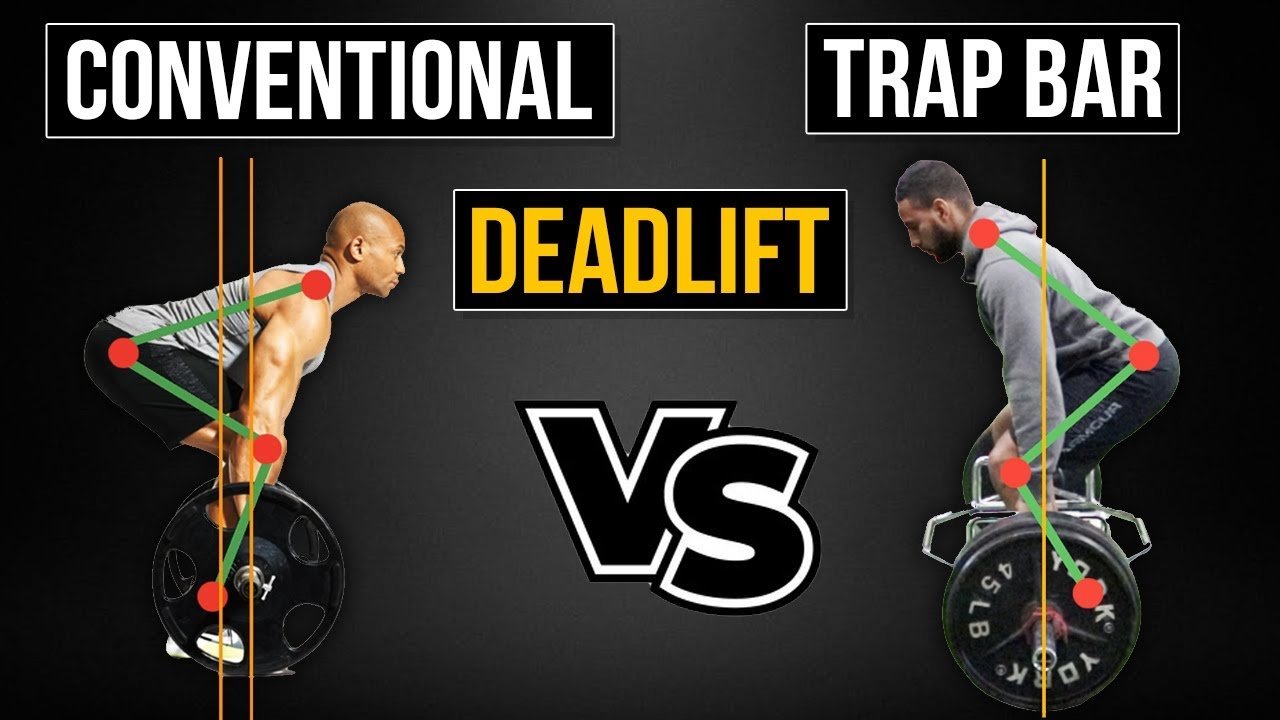
Benefits of Trap Bar Deadlifts
- Reduced Lower Back Stress: The neutral grip and centred load alleviate lower back strain.
- Quad Dominant: Greater activation of the quadriceps.
- Beginner Friendly: Easier to examine and safer for novices.
How to Perform a Trap Bar Deadlift
- Setup: Step within the lure bar and stand with feet hip-width apart.
- Grab the Bar: Bend at the hips and knees and grip the handles.
- Lift: Engage your core, straighten your back, and lift the bar by expanding your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the motion to lower the bar back to the ground with control.
Deficit Deadlift Variations
What is the Deficit Deadlift?
The debt deadlift interests standing on a platform or weight plate to increase the range of motion. This variation emphasizes the quads and lower back.
Benefits of Deficit Deadlifts
- Increases Range of Motion: Enhances flexibility and strength through a more excellent range.
- Targets Quads and Lower Back: Greater activation of these muscle groups.
- Improves Conventional Deadlift Strength: Carries over to improve traditional deadlift performance.
How to Perform a Deficit Deadlift
- Setup: Stand on a platform or weight plate with ft hip-width apart.
- Grab the Bar: Bend at the hips and knees and grip the bar just out of the doors on your knees.
- Lift: Engage your middle, straighten your backpack, and raise the model by expanding your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the movement to decrease the bar and return to the ground with management.
Snatch Grip Deadlift Variations
What is the Snatch Grip Deadlift?
As the clutch elevates, the seizing grip deadlift requires an extensive grasp. This version increases the range of motion, engages the higher back, and traps extra.
Benefits of Snatch Grip Deadlifts
- Upper Back and Trap Activation: Greater emphasis on these muscle groups.
- Increases Range of Motion: Enhances flexibility and strength through an extra variety.
- Improves grip strength: The massive grip demands grip endurance in situations.
How to Perform a Snatch Grip Deadlift
- Setup: Stand with feet hip-width apart and grip the bar with a big, overhand grip.
- Lift: Engage your core, straighten your back, and raise the model by expanding your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the motion to lower the bar back to the ground with control.
Rack Pulls
What are Rack Pulls?
Rack pulls are a partial deadlift variations performed from a raised platform or power rack. This reduces the range of motion and focuses on the top portion of the lift.

Benefits of Rack Pulls
- Reduces Lower Back Stress: Less strain on the decreased back due to the decreased variety of movement.
- Builds Lockout Strength: Targets the muscle mass inside the deadlift’s pinnacle.
- Useful for Injury Prevention: This can educate deadlift mechanics without the overall variety of movement.
How to Perform Rack Pulls
- Setup: Position the barbell at knee height on a rack or platform.
- Grip the Bar: Stand with ft hip-width aside, and grip the streak exceeding your knees.
- Lift: Engage your middle, straighten your lower back, and raise the bar by extending your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the movement to lower the bar again to the rack with manage.
Single-Leg Deadlift Variations
What is the Single-Leg Deadlift?
The unmarried-leg deadlift is a unilateral variation that disturbs conditions balance and coordination. It includes lifting one leg off the floor simultaneously as performing the deadlift motion with the other leg.
Benefits of Single-Leg Deadlifts
- Improves Balance and Coordination: improves proprioception and balance.
- Targets Glutes and Hamstrings: Greater emphasis on one’s muscle organization.
- Reduces Muscle Imbalances: Addresses asymmetries among legs.
How to Perform a Single-Leg Deadlift
- Setup: Stand on one leg and maintain a dumbbell or kettlebell in the other hand.
- Lower the Weight: Hinge at the hips, lower the weight towards the floor while extending the free leg behind you.
- Lift: Engage your glutes and hamstrings to lift the burden lower back to the starting position.
Banded Deadlift Variations
What is the Banded Deadlift?
The banded deadlift involves adding resistance bands to the barbell. This increases resistance as you lift, challenging your muscles differently.
Benefits of Banded Deadlifts
- Accommodates Resistance: Bands increase resistance as you lift, providing constant tension.
- Improves Lockout Strength: Enhances strength in the top portion of the lift.
- Versatile: It can be adapted to various deadlift variations for added challenges.
How to Perform a Banded Deadlift
- Setup: Secure resistance bands to the barbell and anchor them to the ground or a solid item.
- Grip the Bar: Stand with feet hip-width apart and grip the bar just out of the doors on your knees.
- Lift: Engage your core, straighten your returned, and lift the model by expanding your hips and knees.
- Lower: Reverse the motion to lower the bar again to the floor with the manager.
Conclusion
Incorporating one of a kind deadlift versions into your training regimen can provide a well-rounded technique to building electricity, improving muscle mass, and improving general health. Each variation objectives one-of-a-kind muscle businesses and offers precise blessings, permitting you to cope with particular schooling goals and decrease the threat of harm. Whether you are an amateur or a sophisticated lifter, exploring these deadlift versions allows you to acquire your fitness targets and maintain your exercises attractive and powerful.